Biodegradable Waterproof Bags: Eco-Friendly Materials & Future Trends

Introduction
The waterproof bag industry has long relied on synthetic materials such as PVC, TPU, and nylon. These offer strong durability, but with growing demand for eco-friendly waterproof bag materials, many brands are now exploring alternatives. Manufacturers like Vancharli Outdoor are focusing on sustainable waterproof bag manufacturing to meet both performance and environmental requirements.
TIP: The future of waterproof bags is not only about performance—it’s about responsibility.
1. Market Drivers for Eco-Friendly Waterproof Bags
- Consumer Awareness: Growing demand for eco-certified and low-impact products.
- Regulatory Pressure: EU, US, and Asia introducing bans or restrictions on plastics and PFAS.
- Brand Positioning: Outdoor and lifestyle brands using sustainability as a competitive edge.
Market data strongly supports this momentum:
| Metric | Value (2023 / 2024) | Projected (2030 / 2032 / 2034) | CAGR |
| Compostable & biodegradable refuse bags market | ~ USD 374.01 million | ~ USD 610.48 million by 2030 | 7.4% |
| Global biodegradable bags market | — | USD 4.69 billion by 2032 | 9.7% |
| Biodegradable plastics market | USD 12.92 billion (2024) | USD 33.52 billion (2029) | 21.3% |
| Compostable packaging market | USD 103.77 billion (2024) | USD 232.47 billion (2034) | 8.4% |
2. Traditional vs Biodegradable Materials
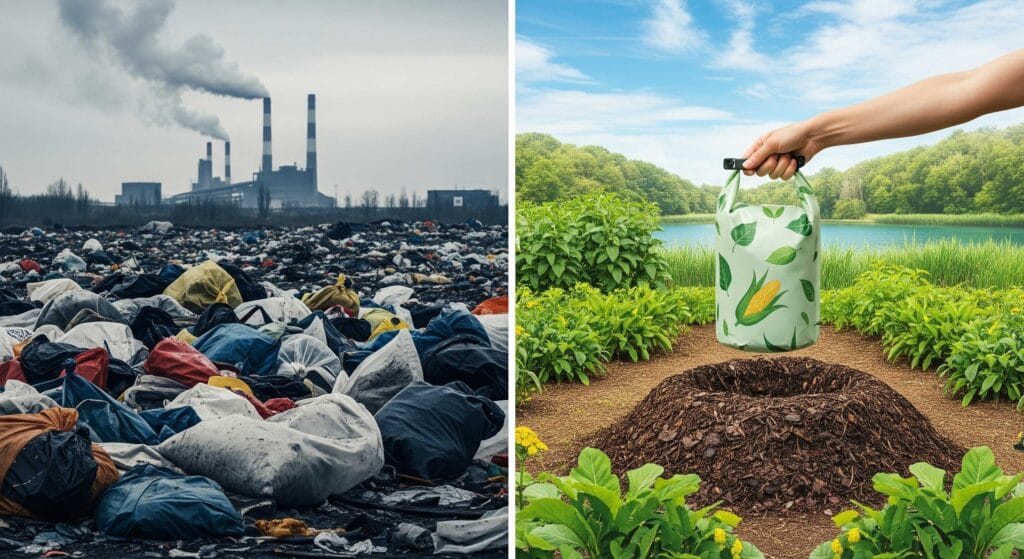

Traditional waterproof materials like PVC, TPU, and nylon have been industry standards for decades. They deliver strong performance but are tied to environmental issues such as landfill persistence and regulatory risks. In contrast, biodegradable waterproof bag materials such as PLA, PHA, PBS, and coated paper aim to reduce this burden.
| Criteria | Traditional Waterproof Materials (PVC, TPU, Nylon) | Biodegradable/Plant-Based Alternatives (PLA, PHA, PBS, Coated Paper) |
| Environmental Impact | Non-biodegradable; persist in landfills/oceans for decades | Break down in compost, soil, or marine environments |
| Carbon Footprint | Petroleum-based, high CO₂ footprint | Renewable feedstock (corn, sugarcane, seaweed) lowers emissions |
| Durability | High abrasion, UV resistance, long-lasting | Moderate; sensitive to heat and UV, improving with blends |
| Waterproof Mechanism | Dense polymer + HF welding or laminated coatings | Bio-based waxes, hybrid coatings, nanocoatings |
| End-of-Life | Difficult to recycle, often incinerated | Compostable or recyclable under industrial systems |
| Regulatory Pressure | Facing bans (PVC, PFAS) in EU/US | Supported by certifications like OK Compost, GRS |
| Applications | Outdoor dry bags, travel backpacks, industrial gear | Compostable packaging, eco-friendly waterproof bags |
| Cost | Relatively low | 30–50% higher, though declining as adoption grows |
Many sustainable waterproof bag OEM suppliers are now using rPET fabrics combined with plant-based waterproof coatings to balance durability with eco performance.
TIP: Buyers should evaluate not just “biodegradable” claims but whether materials perform in IPX waterproof testing.
3. Emerging Biodegradable Materials

The industry is actively testing different eco-friendly waterproof bag materials. Each material has unique strengths and weaknesses:
| Material | Source | Waterproof Potential | Biodegradability | Challenges | Current Use Cases |
| PLA (Polylactic Acid) | Corn, sugarcane | Moderate with coatings | Compostable (industrial) | Brittle, heat-sensitive | Packaging, experimental waterproof panels |
| PHA (Polyhydroxyalkanoates) | Microbial fermentation | Strong for coatings | Biodegradable in soil & water | Expensive, limited supply | Specialty films, pilot outdoor gear |
| PBS (Polybutylene Succinate) | Bio-based succinic acid | Flexible, blendable | Compostable in soil | Cost higher than PLA | Mulch films, laminates |
| Coated Paper + Bio-Wax | Wood pulp + natural wax | Low waterproofing | Fully biodegradable | Weak durability | Compostable shopping bags |
| Seaweed-based Polymers | Seaweed extracts | Hydrophobic potential | Natural biodegradability | Early-stage | Pilot eco-bags, liners |
| rPET + Bio-Coating | Recycled PET + bio layer | Good durability | Not fully biodegradable but reduces virgin plastic | Relies on recycling | Ocean plastic backpacks, hybrid bags |
Research insights:
- Elsevier: Stearic acid additives improved seaweed-based waterproof films.
- MDPI Polymers: Bioplastics degrade differently in compost vs. soil.
- Nature Communications: Not all “biodegradable plastics” degrade in real-world marine environments.
TIP: Hybrid solutions such as rPET + bio-coatings remain the most practical for eco-friendly waterproof bag suppliers in the short term.
4. Case Studies in Eco-Innovation

Examples from the market show how brands are innovating:
1.Got Bag (Germany)
- Uses ocean plastic rPET with eco coatings.
- A prime sustainable waterproof bag OEM case balancing durability with sustainability.
2.Notpla (UK)
- Pioneering seaweed-based waterproof materials for bags.
- Used mainly in packaging, but adaptable for liners in outdoor gear.
3.Patagonia (USA)
- Eliminating PFAS by testing plant-based waterproof coatings for backpacks and jackets.
4.Decathlon (France)
- Testing biodegradable composites in selected product lines.
5.Industry Reviews
- ScienceDirect: Cross-industry cooperation is key to scaling biodegradable waterproof materials.
- Newlong: Bio-based barrier coatings are vital to compostable waterproof solutions.
TIP: Transition will be gradual: recycled plastics → bio coatings → fully compostable waterproof bags.
5. Future Development Directions
The evolution of biodegradable waterproof bags will occur in phases, shaped by technology, regulations, and supply chain shifts.
| Development Path | Advantages | Challenges | Market Outlook |
| Hybrid Materials | Balance eco + durability | Integration complexity | Near-term solution |
| Compostable Linings | Reduce petroleum PU usage | Limited waterproofing | Packaging/light bags |
| Circular Design | Easy disassembly and recycling | Supply chain redesign | Medium-term adoption |
| Standardization | Certifications build trust (GRS, Bluesign) | Cost, lack of harmonization | Critical for B2B procurement |
| Industrial Partnerships | Speeds innovation and scaling | Coordination challenges | Essential for cost reduction |
| Smart Materials | Bio-based nanocoatings, PFAS-free repellents | High R&D cost | Potential breakthrough |
| Policy-Driven Adoption | Plastic/PFAS bans force compliance | Compliance cost | Creates “must-adopt” demand |
| Consumer Education | Builds end-user trust in eco products | Balancing claims vs performance | Strengthens early adopter brands |
For brands and importers, the direction is clear: factories that anticipate regulation, achieve certification, and offer flexible MOQ biodegradable waterproof bag production will dominate procurement.
TIP: The winners will be those who invest early in certified biodegradable waterproof solutions.
Conclusion
Developing waterproof bags with biodegradable waterproof materials is both a challenge and an opportunity. For brands seeking a sustainable waterproof bag OEM supplier with expertise in eco-friendly waterproof backpack manufacturing, Vancharli Outdoor combines 30+ years of production know-how with innovative solutions.
If you need a partner for sustainable waterproof bag production, Vancharli can help bring biodegradable waterproof bags from concept to market.
Final TIP: Early adopters will gain both environmental and market advantages.
FAQ
Q1: What are biodegradable waterproof bags made of?
They are often made from PLA, PHA, PBS, coated paper with bio-based wax, or hybrid fabrics such as rPET with plant-based coatings.
Q2: Are biodegradable waterproof bags as durable as traditional PVC or TPU bags?
Currently, they offer moderate durability. Hybrid designs—such as rPET fabrics with bio-coatings—improve lifespan and performance.
Q3: Why are biodegradable waterproof bags more expensive?
Biodegradable raw materials and coatings cost 30–50% more than petroleum-based plastics, but costs are expected to decrease with scaling.
Q4: What certifications should brands look for in eco-friendly waterproof bags?
Key certifications include GRS, OK Compost, and Bluesign, which verify material traceability, biodegradability, and sustainability.
Q5: Can biodegradable waterproof bags pass IPX waterproof testing?
Some biodegradable bags can reach IPX4–IPX6 levels with bio-coatings, but fully compostable bags often have lower resistance than PVC or TPU.
See Also
Top 10 Waterproof Bag Manufacturers for Outdoor Gear in 2025
Why Are 100% Waterproof Bags So Expensive? Cost Breakdown for Buyers
How to Make Waterproof Bags: The Latest Guide for 2025




Comments are closed