The Difference Between Sewing And Heat Sealing In Outdoor Bag Manufacturing
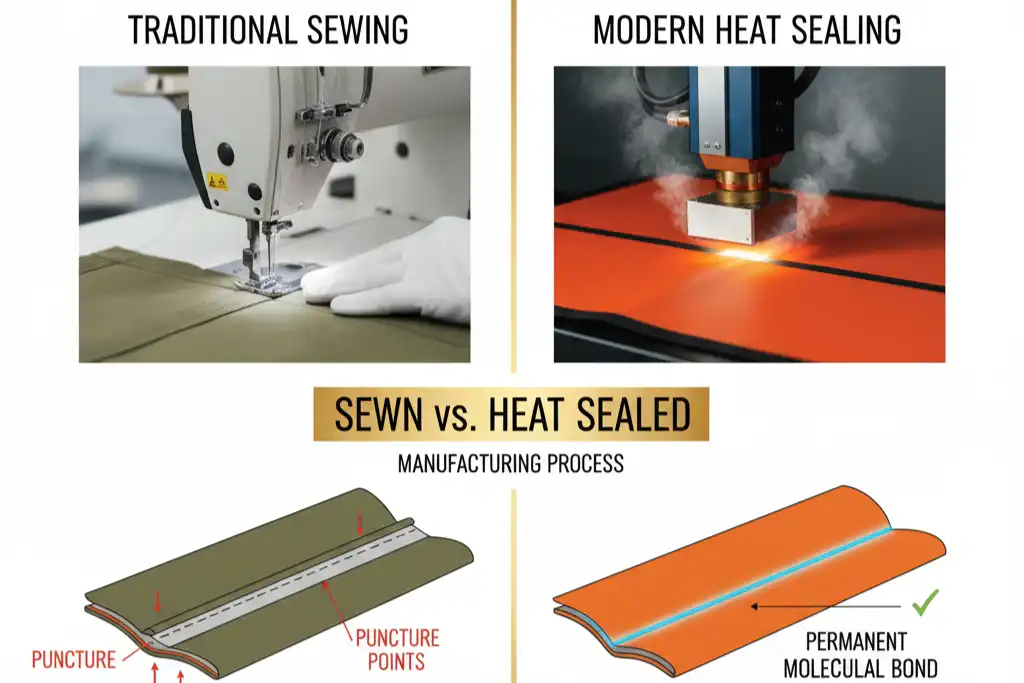
What sets sewing and heat sealing apart in outdoor bag manufacturing? You may look for bags that keep water out, last longer, or fit your budget. Consider these points:
- Sewn seams can let water leak through each stitch, while heat sealing creates a watertight seal.
- Heat sealing usually forms a stronger bond that does not weaken quickly.
- PVC-coated fabrics resist tears and abrasion, and their waterproof rating helps bags survive heavy rain.
Sewing and heat sealing offer unique benefits. Think about which features matter most to you.
Key Takeaways
- Sewing makes tough seams but water can get in. You can seal seams to stop leaks.
- Heat sealing joins fabric without holes, so water cannot pass. This works well for waterproof bags.
- Pick the best way for your bag. Sewing is strong and lets you change designs. Heat sealing is fast and stops leaks.
- Sewing is easy to fix with a needle and thread. Heat sealing needs special tools to repair.
- The fabric you use matters a lot. Use thermoplastic-coated fabric for heat sealing. Use woven fabric for sewing.
Sewing and heat sealing: methods compared
Sewing basics
Sewing is a traditional method for joining fabric. You use a needle and thread to stitch pieces together. This technique works well for outdoor bags because it creates strong seams. You can sew most types of fabric, including polyester and nylon. Sewing lets you make complex shapes and add features like pockets or straps.
Here is how the sewing process works in outdoor bag manufacturing:
- You select the right fabric for your bag.
- You cut the fabric into the needed shapes.
- You use a sewing machine or hand tools to stitch the pieces together.
- You check the seams for strength and neatness.
- You finish the bag by adding zippers, straps, or other features.
Sewing and heat sealing both play important roles in bag production. Sewing stands out for its flexibility and strength, especially for heavy-duty bags.
Tip: Sewing gives you more options for design and repair. You can fix a torn seam with a needle and thread.
Heat sealing basics
Heat sealing uses heat to bond materials together. You apply direct or indirect heat to melt a layer of plastic or synthetic material. The melted layer fuses the pieces, creating a strong and watertight seal. This method works best with thermoplastic-coated fabrics.
The heat sealing process in outdoor bag manufacturing includes these steps:
- You choose a fabric with a thermoplastic coating, such as PVC or polyurethane.
- You cut the material to the correct size.
- You use a heat sealing machine to apply heat and pressure to the seams.
- You allow the seam to cool and set.
- You inspect the seal for leaks or weak spots.
Heat sealing creates smooth seams that block water and air. You often see this method in waterproof bags, dry sacks, and lightweight gear.
Note: Heat sealing is faster than sewing for large batches. You get consistent results with less manual labor.
Material compatibility
Not all fabrics work with both methods. You need to match the sealing technique to the material. Sewing and heat sealing each have their own strengths when it comes to material compatibility.
Here is a table showing which materials work best with each method:
| Material | Compatibility with Sewing | Compatibility with Heat Sealing |
|---|---|---|
| Polyester | High | Moderate |
| Nylon | High | Moderate |
| PTFE | Moderate | High |
| PVC | N/A | High |
| Polyurethane | N/A | High |
You can sew most woven fabrics, such as polyester and nylon. Heat sealing works best with coated or synthetic materials like PVC, PTFE, and polyurethane. If you want a waterproof bag, you should choose a fabric that bonds well with heat sealing.
Regulatory standards also affect your choice. These standards require that bags made from woven flat fabrics must be sewn or closed using a strong method. For tubular fabrics, you must use sewing or an equally strong closure.
Sewing and heat sealing offer different advantages depending on your needs. Sewing gives you flexibility and strength. Heat sealing provides leak-proof seams and fast production.
Durability and strength

Sewn seam durability
Outdoor bags often have stitched seams. These seams hold the panels together. Sewing makes a strong bond. Heavy-duty bags like backpacks use this method. Sewn seams last a long time. They keep their shape when stressed. If you carry heavy things, stitched seams help. They do not tear or stretch easily.
Here is a table that compares stitched seams and heat-sealed seams:
| Feature | Stitched Seams | Heat-Sealed Seams |
|---|---|---|
| Leak Protection | Less reliable; potential weak spots | Superior; watertight bond |
| Durability | High durability but micro-gaps may form | More delicate; prone to punctures |
| Aesthetic Appeal | Classic textile charm | Minimalist, less stylish |
| Performance Under Stress | Holds shape well, but leaks under pressure | Leak-proof if intact, but can breach easily |
Sewn seams can get tiny gaps over time. Water can leak in through these gaps. This happens if the bag faces lots of pressure or rough use. Seam problems come from uneven stitching or wrong needle size. Inconsistent seam allowances also cause issues. Bags used in wet or cold weather may have seams that soak up water or get stiff.
Heat-sealed seam durability
Heat-sealed seams use melted plastic to join panels. This makes a watertight bond. It stops leaks from getting in. This method works best for light bags and dry sacks. Heat-sealed seams block mold. They stay flexible in cold weather. Polypropylene coatings stay strong even when the weather changes.
Heat-sealed seams can be fragile. They might get holes if you overload your bag. Dragging the bag on rough ground can break the seams. Problems happen from bad machine settings or poor adhesive. Dirt under the tape can also cause failure. Watch out for air bubbles or wrinkles during production. Misaligned rollers can make seams weak.
Here is a table showing how weather affects both seam types:
| Environmental Factor | Effect on Sewn Seams | Effect on Heat-Sealed Seams |
|---|---|---|
| High Humidity | Moisture absorption in natural fibers, leading to weakening | Prevents mold growth due to moisture repellence |
| Low Temperature | Can cause rigidity and cracking in natural fibers | Polypropylene remains flexible, maintaining integrity |
| High Temperature | Natural fibers may weaken | Polypropylene has a high melting point, ensuring durability |
Sewing and heat sealing both have strong points. Sewn seams are good for heavy bags that carry weight. Heat-sealed seams work best for light, waterproof gear.
Leak resistance
Water protection with sewing
Bags with stitched seams look classic and feel strong. Sewing makes small holes in the fabric. These holes happen when the needle goes through. Water can get in through these holes. This is more likely in heavy rain or if the bag sits in water. To help stop leaks, makers use special tricks:
- Rain-fly stitches make fewer gaps in the seam.
- Water-resistant threads and Teflon-coated needles make seams tougher.
- Seam sealing with heat tape covers stitches and blocks water.
Outdoor bags often use waterproof lining fabrics. TPU-laminated nylon and PU-coated polyester are common choices. These materials help keep your things dry. Hydrostatic head ratings show how much water a fabric can handle. A rating of 5,000–8,000 mm HH means the bag can handle heavy rain. For bags that go underwater, look for ratings above 10,000 mm HH. Seam sealing is very important for stopping leaks. Even the best fabric can leak if the stitches are not sealed.
Tip: Check if your bag has taped seams. Taped seams help keep your stuff dry in storms.
Leak-proofing with heat sealing
Heat sealing protects bags in a different way. Heat and pressure fuse the fabric together. This makes a watertight bond with no needle holes. Bags with heat-sealed seams usually keep liquids inside. They do this even when stressed. Tests show heat-sealed bags do not leak. Stitched bags let moisture escape after lots of use.
- Heat-sealed seams lower the chance of leaks.
- You get waterproofing right away.
- Mold and moisture cannot get through the fused seam.
If you need a bag for kayaking or boating, heat sealing works best. It gives the best leak resistance. You do not need extra seam tape or special threads. The fused seam blocks water and air. Your gear stays safe and dry.
| Method | Initial Leak Resistance | Long-Term Waterproofing | Maintenance Needs |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sewing (with sealing) | Moderate | High (if taped) | May need resealing |
| Heat Sealing | Superior | Superior | Low |
Both sewing and heat sealing protect your gear. Heat sealing is better for keeping water out.
Aesthetics and cost
Visual differences
When you look at outdoor bags, you notice the seams first. Sewn seams show visible stitches. These stitches give the bag a rugged and functional look. Many people see this style as strong and reliable. Heat-sealed seams look different. You see a smooth, clean edge with no thread. This style feels modern and professional. Brands often use heat sealing to create a sleek appearance.
Here is a table that shows what you see and how it affects your opinion:
| Seam Type | Visual Characteristics | Consumer Perception Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Heat-Sealed | Smooth, consistent edge; clean, professional appearance | Associated with higher quality and better branding |
| Stitch-Sealed | Less polished; rugged, functional look | Appeals to consumers seeking durability and strength |
You may choose a bag based on how it looks. If you want a tough bag for hiking, you might prefer visible stitches. If you want a stylish bag for travel, you may like the smooth seams of heat sealing.
Production and repair costs
Manufacturers use different methods to make outdoor bags. Sewing takes more time and skill. Workers need to guide the fabric and check each stitch. Heat sealing uses machines that bond the material quickly. You get more bags in less time. This speed helps companies save money when making large batches.
Here is a table that compares how fast each method works:
| Process | Speed (bags per minute) |
|---|---|
| Sewing | 4 to 20 |
| Heat Sealing | Up to 20 |
Heat sealing often costs less for big orders. You use fewer workers and finish more bags each hour. Repairs work differently. You can fix a sewn seam with a needle and thread. Heat-sealed seams need special tools or patches. This can make repairs harder for you at home.
Bag production also affects the environment. Textile factories use lots of water and chemicals. Air pollution from these factories can harm health. Dyeing fabrics releases toxins into rivers. Heat sealing with RF welding creates less waste because you only bond the needed area.
- Textile production uses much water and pesticides.
- Factories release air pollution that can cause health problems.
- RF welding reduces material waste.
- Dyeing processes pollute water with heavy metals and toxins.
When you choose a bag, you see the seams, think about the cost, and consider the impact on nature. Each method offers something different for you and the planet.
You can spot big differences between sewing and heat sealing. Sewing makes bags look classic and strong. It works well if you carry heavy things. Heat sealing is fast and keeps water out. But it needs special materials to work. Here is a table to help you compare:
| Method | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| Sewing | Tough, strong, stylish | Takes time, not always waterproof |
| Heat Sealing | Fast, airtight, modern | Needs certain materials, careful use |
Think about what you want most in a bag. Do you care about keeping water out, having strength, or looking cool? If you want to learn more about how bags are made, check out these links:
FAQ
What materials work best for heat sealing outdoor bags?
You should use fabrics with thermoplastic coatings, such as PVC, polyurethane, or PTFE. These materials bond well with heat sealing and keep water out.
What makes heat-sealed seams more waterproof than sewn seams?
Heat-sealed seams fuse the fabric without needle holes. You get a continuous barrier that blocks water. Sewn seams need extra sealing to stay waterproof.
What tools do you need to repair a heat-sealed seam?
You need a heat gun or a special patch kit. These tools melt the patch onto the seam. You cannot fix heat-sealed seams with a needle and thread.
What should you check when choosing between sewing and heat sealing?
You should look at your needs for waterproofing, strength, and budget. Sewing works for heavy-duty bags. Heat sealing is best for lightweight, waterproof gear.



Comments are closed